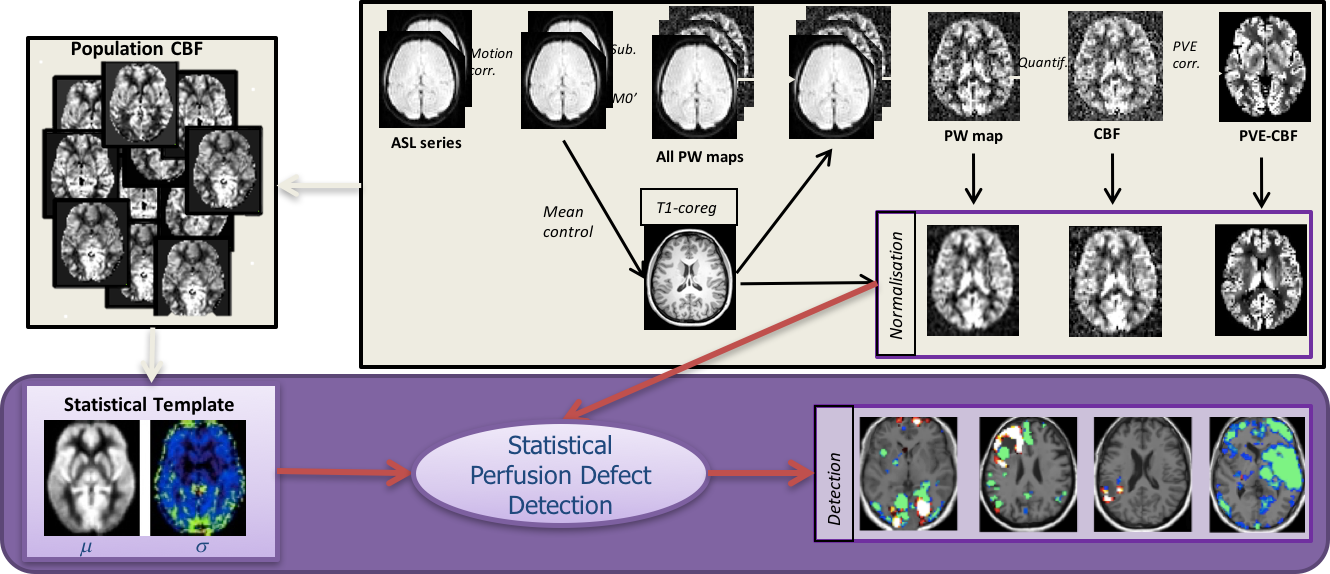
Section: Partnerships and Cooperations
National Initiatives
Projet Fondation de France: PERINE
Participants : Élise Bannier, Isabelle Corouge, Julie Coloigner, Maia Proisy, Jean-Christophe Ferré, Christian Barillot.
This study evaluates the effect of prenatal exposure to neurotoxicants on the developing brain. Following previous studies in the PELAGIE cohort this MRI study involves ASL, Diffusion and working memory as well as motor inhibition BOLD fMRI together with neuropsychological tests in children. Inclusions have started in November 2014 and lasted for 2 years. The MRI acquisitions of the PERINE projects have all been performed with a total of 101 children participating to the project. A collaboration with an external PhD student started in January 2017 to process the functional MRI data of this project and Julie Coloigner was hired as a post-doc to work on the Diffusion and ASL data.
Projet Fondation de France: EPMR-MA
Participants : Pierre-Yves Jonin, Élise Bannier, Christian Barillot, Quentin Duché.
This project evaluates memory effects in healthy adults and in patients presenting cognitive impairments using BOLD fMRI and diffusion MRI. The inclusions of patients started in 2016 and all inclusions will be over by the end of 2017. Quentin Duché was hired to process the functional MRI and diffusion data end of 2016 and his contract was extended until May 2018.
Projet Fondation de France: Connectivity of the amygdala in depression
Participants : Christian Barillot, Jean-Marie Batail, Emmanuel Caruyer, Julie Coloigner, Gabriel Robert.
The onset of depression in teenagers and young adults increases the risk to develop a drug-resistant depression in the adulthood. This project aims at evaluating the role of early changes in the microstructure and connectivity of the amygdala. Using a cohort of drug-resistant patients (N=30), non drug-resistant patients (N=30) and controls (N=30), we will identify imaging biomarkers of the pathology. We will compute the same biomarkers in a group of young adults (N=180) and compare these with emotional and cognitive phenotypes in this population, searching for early differences in the development of the amygdala connectivity.
ANR "MAIA", 2015 generic projects program
Participants : Maia Proisy, Pierre Maurel, Antoine Legouhy, Olivier Commowick, Isabelle Corouge, Jean-Christophe Ferré, Christian Barillot.
Each year in France, 55 000 children are born prematurely, i.e., before the 37th week of gestation. Long-term studies of the outcome of prematurely born infants have clearly documented that the majority of such infants may have significant motor, cognitive, and behavioral deficits.
However, there is a limited understanding of the nature of the cerebral abnormality underlying these adverse neurologic outcomes. In this context, the emergence of new modalities of 3D functional MRI, e.g., Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL), or optical imaging technologies, e.g., Near InfraRed Spectroscopy (NIRS), brings new perspectives for extracting cognitive information, via metabolic activity measures. Other classical techniques devoted to cerebral signal measurement, such as ElectroEncephaloGraphy (EEG), provide cognitive information at the cortical level. Each of these various non-invasive imaging technologies brings substantial and specific information for the understanding of newborn brain development.
This project aims at developing innovative approaches for multi-image / multi-signal analysis, in order to improve neurodevelopment understanding methods. From a fundamental point of view, mathematics and computer science have to be considered in association with imaging physics and medicine, to deal with open issues of signal and image analysis from heterogeneous data (image, signal), considered in the multiphysics contexts related to data acquisition (magnetic, optic, electric signals) and biophysics modeling of the newborn brain. A sustained synergy between all these scientific domains is then necessary.
Finally, the sine qua non condition to reach a better understanding of the coupled morphological- cognitive development of premature newborns, is the development of effective software tools, and their distribution to the whole medical community. The very target of this project will be the design of such software tools for medical image / signal analysis, actually operational in clinical routine, and freely available. Academic researchers and industrial partners are working in close collaboration to reach that ambitious goal.
|
Fondation pour la recherche médicale (FRM) - Project "Hybrid EEG/IRM Neurofeedback for rehabilitation of brain pathologies
Participants : Élise Bannier, Jean-Marie Batail, Isabelle Bonan, Isabelle Corouge, Jean-Christophe Ferré, Jean-Yves Gauvrit, Pierre Maurel, Mathis Fleury, Giulia Lioi, Christian Barillot.
The goal of this project is to make full use of neurofeedback (NF) paradigm in the context of brain rehabilitation. The major breakthrough will come from the coupling associating functional and metabolic information from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) to Electro-encephalography (EEG) to “optimize” the neurofeedback protocol. We propose to combine advanced instrumental devices (Hybrid EEG and MRI platforms), with new hybrid Brain computer interface (BCI) paradigms and new computational models to provide novel therapeutic and neuro-rehabilitation paradigms in some of the major mental and neurological disorders of the developmental and the aging brain (stroke, language disorders, Mood Depressive Disorder (MDD), …). Though the concept of using neurofeedback paradigms for brain therapy has somehow been experimented recently (mostly through case studies), performing neurofeedback through simultaneous fMRI and EEG has almost never been done before so far (two teams in the world including us within the HEMISFER CominLabs project). This project will be conducted through a very complementary set of competences over the different involved teams: VISAGES U1228, HYBRID and PANAMA Teams from Inria/Irisa Rennes and EA 4712 team from U. of Rennes I.
PHRC EMISEP: Evaluation of early spinal cord injury and late physical disability in Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
Participants : Élise Bannier, Christian Barillot, Emmanuel Caruyer, Benoit Combès, Olivier Commowick, Gilles Edan, Jean-Christophe Ferré, Anne Kerbrat, Haykel Snoussi.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is the most frequent acquired neurological disease affecting young adults (1/1000 inhabitants in France) and leading to impairment. Early and well adapted treatment is essential in patients presenting aggressive forms of MS. This PHRC project focusses on physical impairment and especially on the ability to walk. Several studies, whether epidemiologic or based on brain MRI, have shown that several factors were likely to announce aggressive development of the disease, such as age, number of focal lesions on baseline MRI, clinical activity. However, these factors only partially explain physical impairment progression, preventing their use at the individual level. Spinal cord is often affected in MS, as demonstrated in postmortem or imaging studies. Yet, early radiological depiction of spinal cord lesions is not always correlated with clinical symptoms. Preliminary data, on reduced number of patients, and only investigating the cervical spinal cord have shown that diffuse spinal cord injury, observed via diffusion or magnetisation transfer imaging, would be correlated with physical impairment as evaluated by the EDSS score. Besides, the role of early spinal cord affection (first two years) in the evolution of physical impairment remains unknown.
In this project, we propose to address these different issues and perform a longitudinal study on Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS) patients, recruited in the first year of the disease. Our goal is to show that diffuse and focal lesions detected spinal cord MRI in the first 2 years can be used to predict disease evolution and physical impairment at 5 years. Twelve centers are involved in the study to include 80 patients.
To date, all subjects have been included. H. Snoussi is working in the scope of his PhD thesis on diffusion imaging in the spinal cord starting with distortion correction.
B. Combès started as a post-doc in November 2016 to process the EMISEP imaging data, starting with morphological data processing (registration, segmentation) and magnetization transfer data processing.
Competitivity Clusters
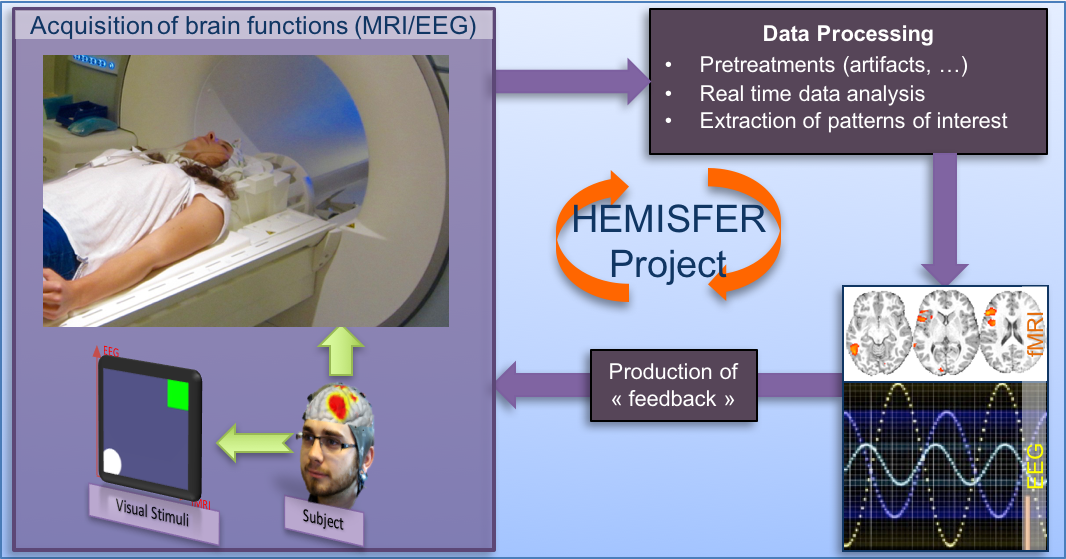
The HEMISFER Project
Participants : Élise Bannier, Jean-Marie Batail, Isabelle Bonan, Isabelle Corouge, Claire Cury, Jean-Christophe Ferré, Jean-Yves Gauvrit, Pierre Maurel, Christian Barillot.
The HEMISFER project ("Hybrid Eeg-MrI and Simultaneous neuro-FEedback for brain Rehabilitation") will be conducted at Inria Rennes with the support of the Cluster of Excellence "CominLabs" (https://iww.inria.fr/cominlabs-newsletter/april-2013-four-projects-selected/#hemisfer). The goal of HEMISFER is to make full use of the neurofeedback paradigm in the context of rehabilitation and psychiatric disorders. The major breakthrough will come from the use of a coupling model associating functional and metabolic information from Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) to Electro-encephalography (EEG) to "enhance" the neurofeedback protocol. We propose to combine advanced instrumental devices (Hybrid EEG and MRI platforms), with new man-machine interface paradigms (Brain computer interface and serious gaming) and new computational models (source separation, sparse representations and machine learning) to provide novel therapeutic and neuro-rehabilitation paradigms in some of the major neurological and psychiatric disorders of the developmental and the aging brain (stroke, attention-deficit disorder, language disorders, treatment-resistant mood disorders, etc.). This project will be conducted with the HYBRID and PANAMA Teams from Inria Rennes, the EA 4712 team from University of Rennes I and the ATHENA team from Inria Sophia-Antipolis. This work will benefit from the research 3T MRI and MRI-compatible EEG systems provided by the NeurInfo in-vivo neuroimaging platform on which these new research protocols will be set up. A budget of 500K€ provided by the CominLabs cluster to support this project (through experimental designs, PhDs, post-docs and expert engineers).
France Life Imaging (FLI)
Participants : Christian Barillot, Olivier Commowick, Michael Kain, Florent Leray, Julien Louis, Aneta Morawin, Mathieu Simon, Yao Chi.
France Life Imaging (FLI) is a proposed large-scale research infrastructure project aimed at establishing a coordinated and harmonized network of biomedical imaging in France. This project was recently selected by the call “Investissements d’Avenir - Infrastructure en Biologie et Santé”. One node of this project is the node Information Analysis and Management (IAM), a transversal node build by a consortium of teams that will contribute to the construction of a network for data storage and information processing. Instead of building yet other dedicated facilities, the IAM node will use already existing data storage and information processing facilities (LaTIM Brest; CREATIS Lyon; CIC-IT Nancy; VisAGeS U1228 Inria Rennes; CATI CEA Saclay; LSIIT/ICube Strasbourg) that will increase their capacities for the FLI infrastructure. Inter-connections and access to services will be achieved through a dedicated software platform that will be developed based on the expertise gained through successful existing developments. The IAM node has several goals. It aims first at building a versatile facility for data management that will inter-connect the data production sites and data processing for which state-of-the-art solutions, hardware and software, will be available to infrastructure users. Modular solutions are preferred to accommodate the large variety of modalities acquisitions, scientific problems, data size, and adapted for future challenges. Second, it aims at offering the latest development that will be made available to image processing research teams. The team VisAGeS fulfills multiple roles in this nation-wide project. Christian Barillot is the chair of the node IAM, Olivier Commowick is participating in the working group workflow and image processing and Michael Kain the technical manager. Apart from the team members, software solutions like MedInria and Shanoir will be part of the final software platform.
OFSEP
Participants : Élise Bannier, Christian Barillot, Olivier Commowick, Gilles Edan, Jean-Christophe Ferré, Michael Kain, Inès Fakhfakh.
The French Observatory of Multiple Sclerosis (OFSEP) is one of 10 projects selected in January 2011 in response to the call for proposal in the “Investissements d’Avenir - Cohorts 2010” program launched by the French Government. It allows support from the National Agency for Research (ANR) of approximately € 10 million for 10 years. It is coordinated by the Department of Neurology at the Neurological Hospital Pierre Wertheimer in Lyon (Professor Christian Confavreux), and it is supported by the EDMUS Foundation against multiple sclerosis, the University Claude Bernard Lyon 1 and the Hospices Civils de Lyon. OFSEP is based on a network of neurologists and radiologists distributed throughout the French territory and linked to 61 centers. OFSEP national cohort includes more than 50,000 people with Multiple Sclerosis, approximately half of the patients residing in France. The generalization of longitudinal monitoring and systematic association of clinical data and neuroimaging data is one of the objectives of OFSEP in order to improve the quality, efficiency and safety of care and promote clinical, basic and translational research in MS. For the concern of data management, the Shanoir platform of Inria has been retained to manage the imaging data of the National OFSEP cohort in multiple sclerosis.